Cyberbullying continues to be a serious challenge in schools, directly impacting students’ emotional well-being and their ability to learn in a safe environment.
In today’s connected world, educators and administrators play a critical role in addressing cyberbullying and fostering a culture of respect and responsibility online.
This comprehensive guide will provide insights, strategies, and resources to equip educators to combat cyberbullying effectively.
What is Cyberbullying?
At its core, cyberbullying is the use of digital media, such as apps, text messages, and websites, to intimidate, upset, or harm someone.
It includes actions like repeatedly sending, posting, or sharing negative, harmful, or mean content about someone else with the intent to hurt or humiliate them.
One significant difference between cyberbullying and traditional bullying is its reach.
Cyberbullying can occur anytime and anywhere, making it challenging to escape. It’s often harder to detect since much of kids’ digital media use goes unmonitored by adults.
At the same time, cyberbullying can be highly public, with large numbers of people witnessing the events and potentially joining in. Anonymity is another characteristic; perpetrators may hide their identity by posting anonymously or using pseudonyms.

10 Types of Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying takes many forms, each with its unique characteristics and potential harm. Understanding these types is essential to identifying and addressing them effectively.
Here are 10 common types of cyberbullying:
- Exclusion: Deliberately leaving someone out of social groups, parties, or online conversations.
- Harassment: Repeatedly sending hurtful or threatening online messages that can cause severe emotional distress.
- Outing/Doxing: Sharing someone’s private information or photos without consent to embarrass or harm them.
- Trickery: Gaining someone’s trust only to reveal their secrets or private information publicly.
- Cyberstalking: Persistent online harassment that may include threats of physical harm. This is illegal and can have serious legal consequences.
- Fraping: Using someone else’s social media accounts to post inappropriate or offensive content.
- Masquerading: Creating fake profiles to deceive and bully others, often by someone the victim already knows.
- Dissing: Spreading cruel rumours or messages to damage someone’s reputation or relationships.
- Trolling: Posting intentionally offensive or hurtful comments to provoke emotional reactions.
- Flaming: Posting direct insults and offensive language aimed at inciting online fights and causing distress.
How Common is Cyberbullying?
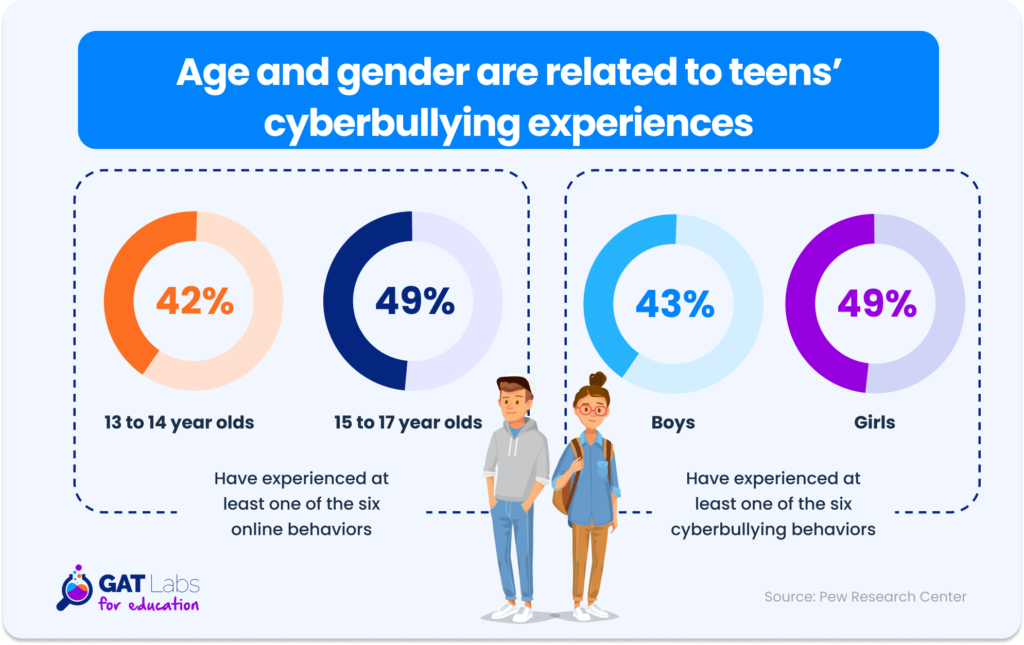
According to a report, nearly half (46%) of teens reported experiencing at least one type of cyberbullying, with 28% experiencing multiple types.
A summary of research from the Cyberbullying Research Center indicated that, on average, 29% of students had been targets of cyberbullying, while nearly 16% admitted to cyberbullying others.
Impact on Mental Health
Data from the CDC’s 2023 Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) underscores the profound mental health implications of cyberbullying. Female and LGBTQ+ students reported higher rates of poor mental health, experiences of violence, and suicidal thoughts. These findings emphasize the need for targeted interventions to support these vulnerable groups.
Detecting and Recognizing It
Educators can play a critical role in recognizing signs that a student may be a victim of cyberbullying.
Pay attention to changes in students’ emotional states, such as depression, fearfulness, or distraction. Be aware of shifts in social dynamics, such as altered friend groups or conflicts among students. Engage in open communication with students, providing a safe space for them to discuss their experiences.
Preventive Measures
Preventing cyberbullying starts with creating a positive, safe classroom environment.
▪️ Support School-Wide Initiatives: Advocate for digital citizenship programs to ensure consistent messaging and support across all grades.
▪️ Promote Digital Citizenship: Teach students the importance of keeping personal information private and using privacy controls.
▪️ Encourage Responsible Online Behaviour: Help students understand the impact of their words and actions online.
▪️ Teach Response Strategies: Encourage them to avoid responding to harmful comments and to report inappropriate content.
▪️ Include Cyberbullying in the Curriculum: Integrate lessons about cyberbullying and responsible online behaviour across various subjects.
Lesson Plans and Classroom Resources
There are several trusted resources to help schools educate students on cyberbullying prevention:
✔️Common Sense Education: Offers a K–12 Digital Citizenship Curriculum, with comprehensive lessons on recognizing and preventing cyberbullying.
✔️ Google’s Be Internet Awesome: An interactive program that teaches students the fundamentals of digital safety and responsible online behaviour.
GAT Shield: Keeping Students Safe Online
In the relentless battle against cyberbullying and ensuring online safety in schools, GAT Shield stands as a powerful ally.
While GAT Labs offers a comprehensive Education Suite, GAT Shield takes the lead in fortifying digital security within your Google Workspace Domain.
Most notably, it keeps a vigilant eye on your students’ online activities, specifically targeting cyberbullying incidents.
Key Features:
▪️ Alerts: Instantly receive notifications concerning online behaviors, such as bad language or threats, to intervene promptly.
▪️ Browsing: Investigate a specific activity for any user, on any site, and at any time. See the exact device and location from which the activity occurred.
▪️ URL Filtering: Use our powerful filtering options to create policies that block sites, access to personal Gmail, and Hangouts, as well as entire site categories.
With GAT Shield as your partner, you can actively combat cyberbullying and uphold online safety for your students.

Conclusion
Addressing cyberbullying in schools is a collective responsibility, and educators are at the forefront of creating a safer online environment for students. By recognizing the signs, intervening effectively, and prioritizing prevention through education, we can combat cyberbullying and ensure that our schools are places where every student can thrive, both online and offline.
Together, let’s make a stand against cyberbullying and empower our students to become responsible digital citizens.
Join our newsletter for practical tips on managing, securing, and getting the most out of Google Workspace, designed with Admins and IT teams in mind.





