This guide is for administrators. You need a Google Workspace Admin account to perform most of the actions recommended below.
”This important Google Drive file disappeared. How do I get it back, and why did it happen?” — A question we receive quite often from Google Workspace admins.
If your company uses Google’s “Loch Ness monster” aka Google Drive, then it’s probably the spine that holds up your valuable data resources and powers other limbs of your organization’s operations.
Unfortunately, with all of the cross-employee collaboration happening there, especially within Shared Drives, it’s not uncommon for files to ‘seemingly’ go missing from your Drive repository.
This can bring in multiple Data loss and Information security concerns (SEE: 6 Google Drive Data Loss Prevention Practices Every CIO Must Know for more).
That’s why we created this simplified guide to help admins understand exactly what happened to those files, and how to recover them (if possible).
Let’s find that missing Google Drive File!
Firstly, we’ll start with the most basic Google Drive File Recovery scenarios and build our way up to File Recovery PRO.
1. Recover a deleted file from the Trash
The easiest most basic scenario: a user moved a file to the trash.
- Visit your Trash folder.
- Right-click on the file you’d like to recover.
- Click Restore.
Note: Files in the trash will be automatically deleted after 30 days. You can restore files from your trash before the 30-day time window. You can also permanently delete them to empty your trash.
2. Recover Permanently Deleted Files in Drive
Did you say ‘Permanently’ deleted? — Is it gone forever? Luckily, no.
There’s a 25 Days File Recovery Window
Google Workspace Admins can recover permanently deleted Drive files and folders within 25 days of deletion from the Trash using the admin console. After that, these files disappear from Google’s systems.
To recover them simply follow these file recovery steps.
Note: Drive data restores to the user’s Drive folder in the same location.
Using Google Vault?
Google Vault is a crucial feature within Google Workspace that grants administrators the ability to search and manage data across their G Suite accounts. With its comprehensive search capabilities, Google Vault empowers admins to locate relevant information not only within their own Google Workspace account but also within their employee’s accounts.
If your organization uses Google Vault you may be able to retrieve data older than 25 days (if it was subject to retention rules or holds).
In that case, you can export the missing data, however, you can’t directly restore it to the user’s Drive. Read more.
3. Recover Files in Shared Drive
Since files in Shared drives belong to ALL team members rather than a single individual, even if members leave, files stay exactly where they are for other team members to continue sharing the data.
However, it can sometimes get pretty messy — That’s why you need to pay attention to TWO key factors:
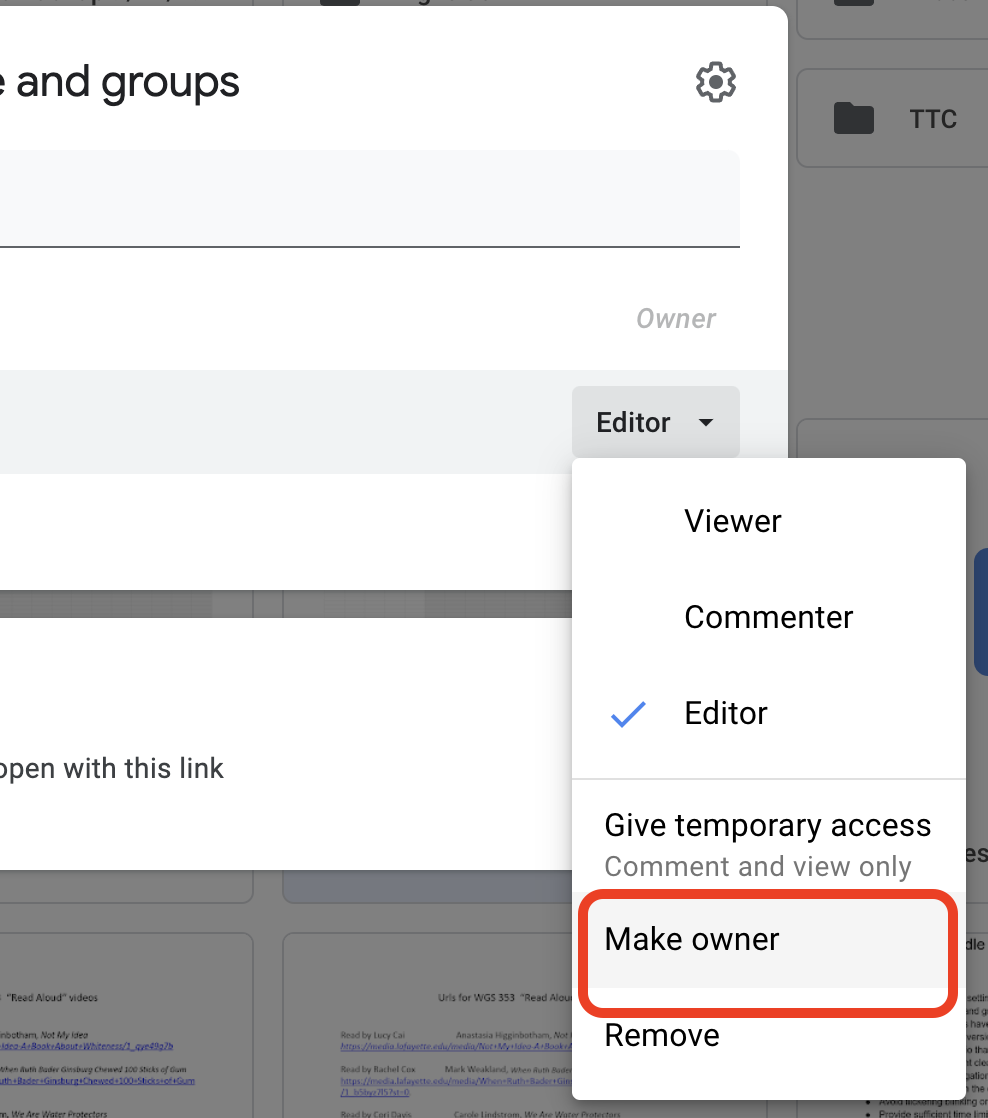
- File Ownership: When it comes to Drive file recovery, file ownership is a crucial factor (Check out our blog: Manage Google Drive File Ownership like a Security PRO for more on that).
- Shared Drive(s) Structure: How you structure your organization’s Shared Drive is also very important. It’s one of the first pillars of a complete Drive DLP strategy.
Deleting Files/ Folders in a Shared Google Drive
Depending on users’ access rights, they may be able to remove files stored in Shared Drives. This can result in Orphaned Drive files (harder to find), which we’ll discuss in more detail below.
4. Noting yet? — Check your Google Drive Audit Log
Not sure if somebody deleted the file in the first place? Visit your Drive audit log, let’s see what you can find there.
This should provide you with information on users’ Drive activity, which may offer some insight into what happened to your missing file or folder.
You can also find information there on files automatically deleted by Drive or emptied from Trash.
Then, you can also use GAT+ to locate files and folders across your entire ‘domain Drive’, and get more granular insights beyond those available in the admin console.
Finally, remember that for ‘My Drives’ users can easily check the ‘Drive activity panel’ to find out more about their missing files/ folders.
5. Check if it’s an Orphaned Drive File now
Sometimes, when you’ve exhausted all your options, it’s time to consider that the file may have been Orphaned.
These files are homeless files created when someone (NOT the file owner) deletes a shared file or folder in Google Drive.
The file then loses its parent folder, becomes ‘homeless’, and thus harder to find.
How to find and rehome Orphaned Files?
There are 3 different ways to recover Orphaned Files:
- Know the file’s name? Search directly using the ”Drive Search”.
- Go to Drive on a computer> log in with your Google account.
- Go to Search> Search for the file by entering its name. It will appear in the results of the search, even if it’s not in any folder.
- You can then rehome it to any folder you choose.
2. Don’t know the file’s name? Use parameters in the Drive search.
-
- Go to Drive on a computer> log in with your Google account.
- Go to Search> search for the following special parameters: is: unorganized owner: me (By adding owner: me, only the files that you have created that are not in a folder will come out).
3. Find Orphaned Files Using GAT+
-
- GAT+ displays the folder structure for each user, this allows Admins to easily find all orphaned files for any user, group, or OU faster.
6. Recover Files from a Deleted/Closed Account
When an account that OWNS a Drive file is deleted, that file is deleted as well — even if it was shared with other domain users.
Perhaps the file belonged to a deleted or closed Google Workspace account.
Lost important files on a Google account that’s now closed? No problem, basically follow the steps Google outlines here.
File Ownership vs Sharing in Google Drive
Finally, let’s look into why file ownership is a crucial factor to consider when searching for missing files in Google Drive.
Files are bound to their owners, not others with whom the file is shared with. Understanding file ownership helps you solve the bigger riddle better by knowing where exactly to look.
A. File Ownership:
Every file (or folder) a user creates, syncs, or uploads automatically becomes its Owner. As the owner, they can:
- Share it with other people.
- Permanently delete it from Google Drive.
- Control whether people can edit, comment on, or only view the file.
- Transfer ownership to someone else.
B. File Sharing:
Whenever the user shared a file (or folder) in Google Drive, that file (or folder) still remains with the owner (on their Drive).
Now if the owner deletes the file, it will physically delete the file from the Drive. As a result, those users with whom the file is shared will no longer have access to it.
Contributors Can’t:
- Delete a file shared with them because only the owner can delete the file for good.
- Recover a file shared with them that the owner deleted.
What if someone shares a file with another user, that user adds it to their Drive, then later deletes it? Will it still be on their Drive?
The answer is No. The file is still ‘owned’ by the person who created it. All they did there was reorganize the file in their own Drive, so they can still find it. That’s different from copying or downloading it.
Finding files that contain sensitive information in Google Drive faster
When using GAT+, an admin can find any document from the domain that contains sensitive data, here’s how.
As a result, you can perform a search in Drive for all your domain users in bulk and find faster files that contain critical data to better manage and secure them.
10 more ways GAT helps you better manage Google recovery – Drive file ownership and sharing:
- Replace current sharing permissions on your Google Drive files.
- Removing all permissions on Drive shares with an exception of a single user.
- Find publicly shared Google files.
- Search for specific File types in your domain and change their ownership in Google Drive.
- Manage files owned by leaving users easily.
- Remove all permissions to all sensitive folders and their sub-folders.
- Understand Google Group activity email and file sharing.
- Remove external shares when files haven’t been accessed for a certain number of days.
- Prevent MP3 files and other file types from being downloaded.
- Detect a sharing Policy Violation in Drive.
You’ve reached the end of your ultimate Google Workspace File Recovery 101 guide! We hope you found it immensely helpful.
Editor’s Note: This blog was originally written in November 2021 and has been updated to provide the most current and accurate information regarding Google Workspace File Recovery. We strive to keep our content relevant and up-to-date to ensure you receive the best guidance for your administrative needs.
For any lingering questions, reach out to our experts at hello@gatlabs.com.
Happy recovering!
Insights That Matter. In Your Inbox.
Join our newsletter for practical tips on managing, securing, and getting the most out of Google Workspace, designed with Admins and IT teams in mind.